Radon AI
Radon AI is a dedicated React Native AI assistant enhanced with up-to-date information about the React Native ecosystem. At its heart is our extensive React Native knowledge database, which is queried before answering your question.
We index all of the popular React Native libraries to match questions to relevant pieces of documentation, providing additional, accurate context to your conversation.
Our knowledge database is updated daily to provide the most up-to-date information.
Pre-requisites
- Cursor Editor or Visual Studio Code 1.99 or newer
- In Visual Studio Code: Access to GitHub Copilot and GitHub Copilot Chat. GitHub Copilot Chat comes with a GitHub Copilot Free without needing to sign up for another subscription.
- An active Radon IDE license
Usage in Visual Studio Code
You can use Radon AI in Visual Studio Code as a GitHub Copilot Chat participant or via Model Context Protocol (MCP) server in the agent mode.
Use Radon AI as Copilot Chat participant
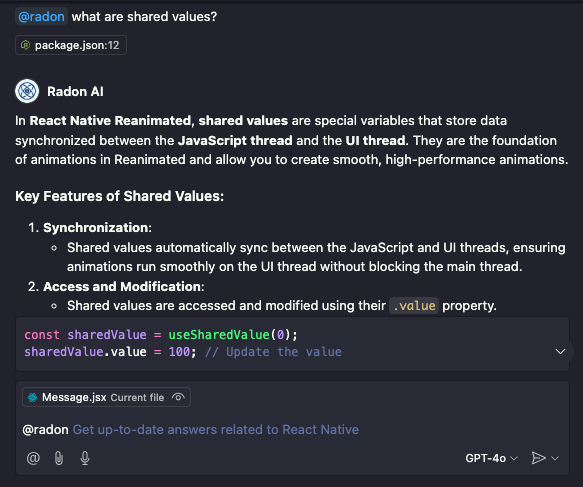
To start chatting with Radon AI open the GitHub Copilot Chat panel.
Open the vscode command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P) and type "Chat: Open Chat" or "Radon IDE: Chat with Radon AI" and select the command.
Messages that you want to send to Radon AI need to be started with @radon prefix.
Radon AI has the context of the history of previous messages sent in the chat window started with @radon. This allows you to send additional follow-up questions.
To start a new conversation open a new chat window.
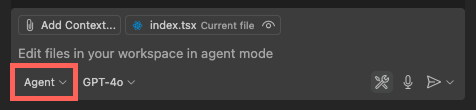
Use Radon AI in agent mode
Radon IDE automatically configures and activates Radon AI MCP server for you. Also, VS Code respect the mcp.json config from other editors (e.g. .cursor/mcp.json) and configuration through .vscode/mcp.json.
To access agent mode in Visual Studio code use Ctrl+Shift+I or Cmd+Shift+I.
Alternatively, open vscode command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P) and type "Chat: Open Chat" then select agent mode.
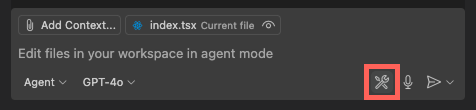
To adjust the configuration of the MCP server choose Configure Tools... menu.
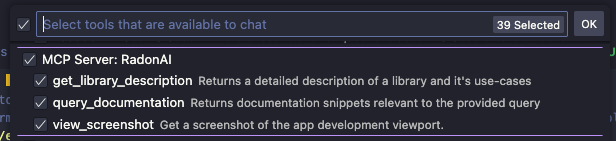
There you can adjust which tools are enabled or disable the Radon AI MCP server completely.
Usage in Cursor
Radon AI is disabled in Cursor by default.
To enable it, go to the Settings -> VS Code Settings tab (Cmd + , or Ctrl + ,), type Radon AI: Enabled into the search bar, press the first result and select Enabled.
Radon AI assistant integrates with Cursor's agent mode via Model Context Protocol (MCP) server.
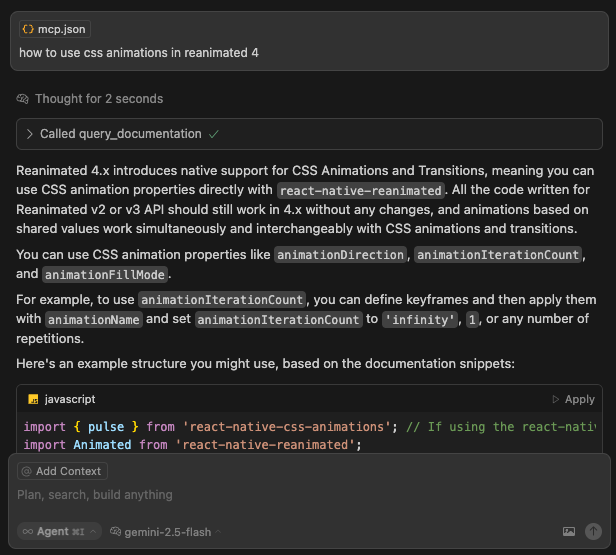
The Radon IDE automatically adds the Radon AI MCP server configuration by creating a .cursor/mcp.json or appending an entry if this file exists. Cursor detects this change and asks you to enable the server.
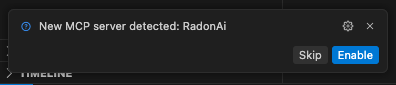
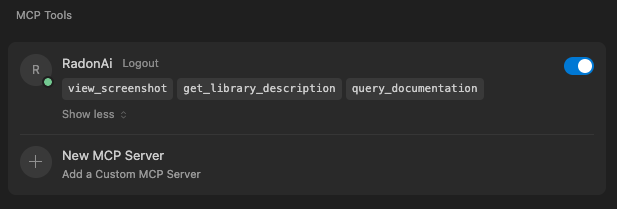
You can to configure the Radon AI MCP server from Cursor Settings. There, you can adjust the server configuration, choose which tools are enabled or disable the MCP server completely.
- In Cursor, open
Cursor Settings(Ctrl+Shift+J or Cmd+Shift+J). - Navigate to the
Tools & Integrations. - Find the
MCP Toolssection. - Select
Radon AIfrom the list of available servers.
Alternatively, you can type and run "View: Open MCP Settings" from the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P).
Available tools
The AI models automatically discover and invoke tools when they decide it will be useful. You can query the agent to use the tool by mentioning it's name in the prompt. These are currently available tools in Radon AI:
get_library_descriptionProvides a detailed description of a library and its use cases.query_documentationRetrieves documentation snippets relevant to a provided query.view_application_logsReturns all the build, bundling and runtime logs available to Radon IDE. If the app builds and launches successfully, this tool will also attach a screenshot of the app.view_screenshotCaptures a device preview screenshot. Can help the agent with debugging issues and making UI adjustments. Currently only supported in GPT, Gemini and Claude models.view_component_treeDisplays the component tree of the running app. This tool allows the agent to gain a broad understanding of the project's structure.
Limitations
-
Radon AI will refuse answering questions outside of the React Native and Expo domain.
-
Like any technology based on large language models, Radon AI is prone to errors. Make sure to check important information before making decisions.
-
Currently (June 2025), the knowledge base used by Radon AI contains only documentation files. While some documentation pages contain code snippets, we do not index the full source code of the libraries. For this reason, the React Native code generated by Radon AI may not be accurate.
-
GitHub Copilot Free is limited to 50 chat messages per month. When you reach this limit, you can upgrade to Copilot Pro to continue using Radon AI.
Changing mcp.json write location
To change the location of mcp.json file, navigate to the editor settings.
Open the command palette by pressing Cmd+Shift+P (or Ctrl+Shift+P on Linux and Windows), then type "Preferences: Open User Settings".
Within editor settings, type "Radon IDE: Location Of Mcp Config" and choose whether the server entry should be written to the project's .cursor directory, or the global ~/.cursor directory.
Disabling Radon AI
To disable Radon AI assistant navigate to the editor settings.
You can type "Preferences: Open User Settings" in the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P).
Within editor settings, type "Radon AI: Enabled", press the first result and select Disabled.
Privacy
To provide accurate responses, queries that you type to Radon AI chatbot along with the list of your project dependencies are sent to our servers in order to search our knowledge database. The data that is sent is not stored in any form on our servers but only used for the duration of the request in order to perform the query.